Planning and Completing Your OER Project
Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Identify the 5 main steps of the OER creation process
Each OER project is different and rarely is an OER adoption a turn-key process. While OER textbooks exist for many high-enrollment courses, the pedagogical design (or teaching style) and student population will vary.[1]
OER PRODUCTION FRAMEWORK
The following OER production framework, based on an instructional design framework, depicts the major steps that OER adoptions typically go through:
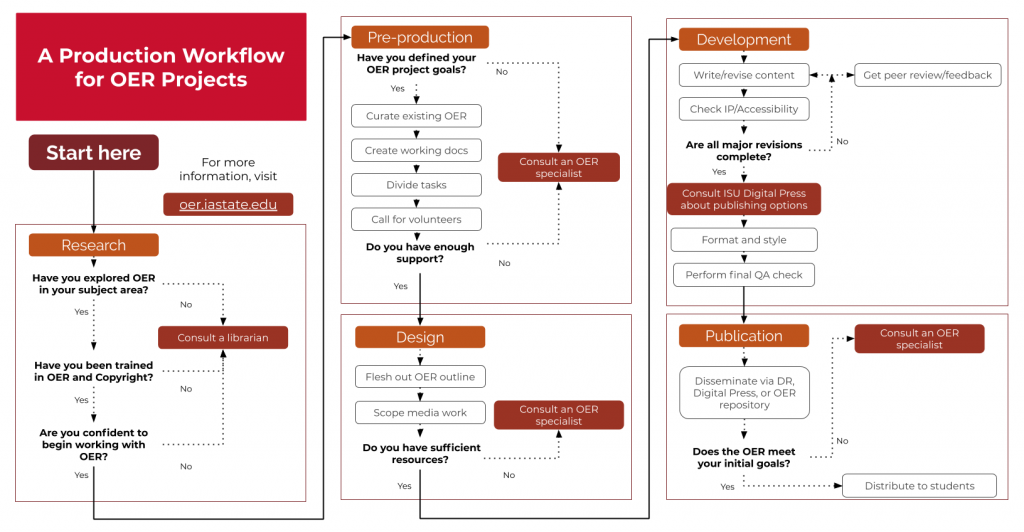
You can see the full Project Production Workflow on Google Drawings.
Priming phase
At this step, you should ask yourself a few key questions to gauge your OER knowledge and skills before taking on a project. Have you explored OER content in your subject area? Have you been though any previous training for work with OER in the past? Contact support staff on campus to receive any training you might be lacking for working with open content.
Pre-production phase
This phase involves the curation of existing resources that may be applicable to the OER adoption and planning out the general design of the project. No new content should be adapted in this step, but a skeleton outline and other time-and-task-based project management documents should be prepared. Getting an OER consultation scheduled at this time is encouraged.
Design phase
This step is the last planning phase before work on the actual OER content begins. For projects adapting OER as-is, this may be the final step apart from preparing instructional documents. During this phase, project outlines and skeleton documents are fleshed out, and existing OER are fit into places where they are believed to be applicable. Any visual/graphic design work and processes that require assistance from an instructional designer are included here.
Development phase
This phase is where the most time is spent on OER projects that require building new materials. Existing OER that are being adapted or modified go through revision and review in a closed loop until they are in a place where they require only minor changes or copyedits. Checks for intellectual property (which CC license is on the content, and have we appropriately attributed everything?) are done, as well as checks for accessibility (is content formatted semantically, do images include alt-text, etc)?
Content here is typically drafted in Google Docs or another rich content editor (Word, OpenOffice) and are then ported into the publishing platform (the ISU Digital Press recommends Pressbooks for text-based content).
Publishing phase
The final phase involves publishing and sharing the content that has been created. This includes creating export versions, archiving editable files for instructors who might wish to edit your work (.doc, .xml, etc), and depositing any ancillary materials such as syllabi or lesson plans in the institutional Digital Repository. The new adapted or original OER content is then disseminated to learners and shared with the open community.
- Planning & Completing your OER Project was adapted from Scoping an OER Project by Billy Meinke, licensed CC BY 4.0. ↵

